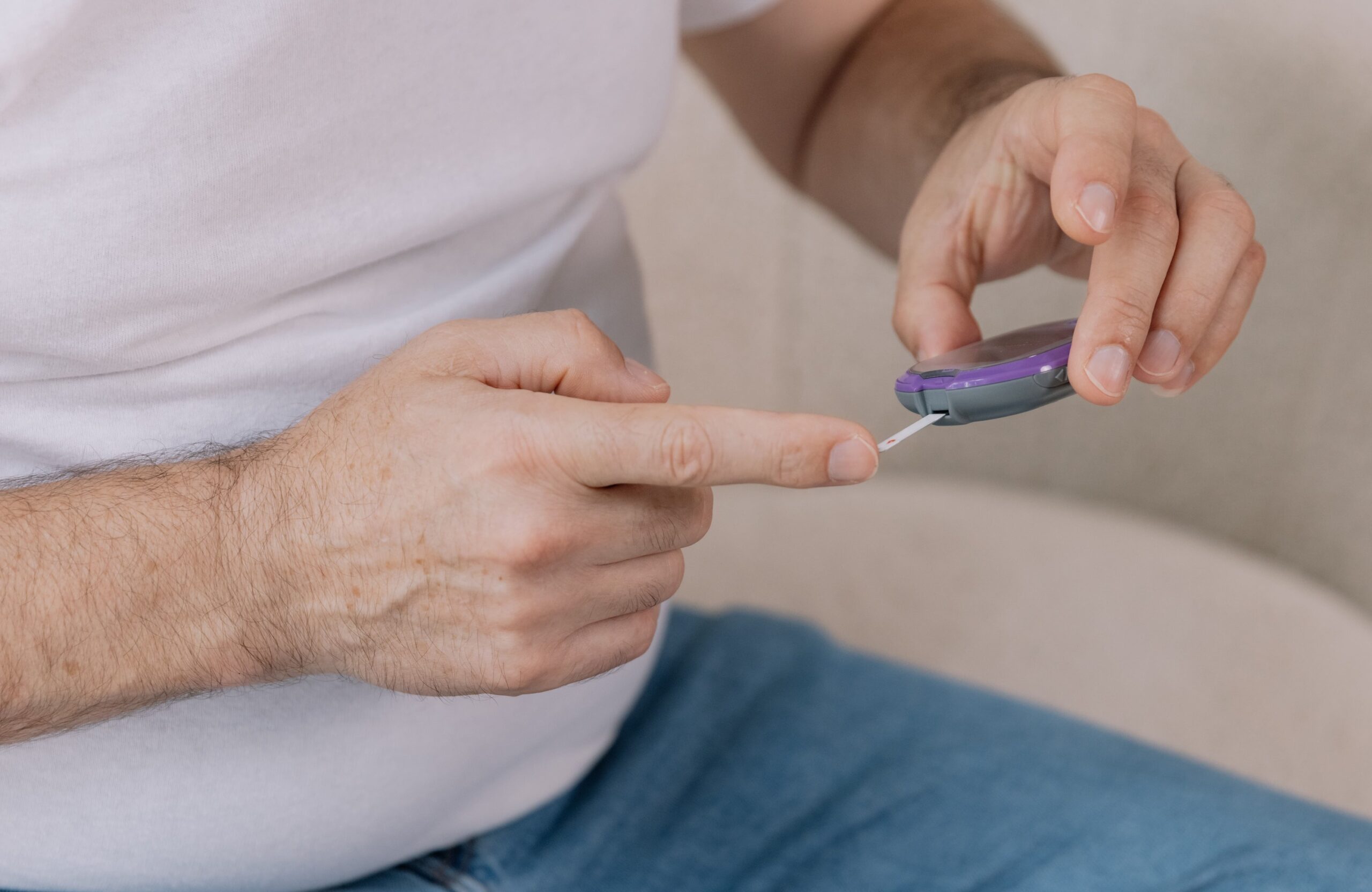
Effective blood glucose control combines lifestyle adjustments with medical supervision. Regular physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and supports a healthy weight. A balanced diet with consistent carbohydrate intake helps stabilise blood sugar levels, aided by meal planning and portion control. Routine medical check-ups allow early detection and treatment of complications. Managing stress through techniques like mindfulness or relaxation exercises also helps minimise blood sugar fluctuations.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes symptoms can vary between individuals, but several common signs may indicate the condition.
-
Increased Thirst and Urination
High blood sugar levels prompt the kidneys to expel excess glucose through urine, leading to dehydration and heightened thirst.
-
Unexplained Weight Changes
When cells cannot access glucose for energy, the body breaks down fat and muscle, causing weight loss despite normal eating habits.
-
Fatigue
An energy deficit caused by insufficient glucose uptake by cells results in persistent tiredness and weakness.
-
Blurred Vision
Elevated blood sugar levels can temporarily swell the lens of the eye, impairing visual clarity and focus.
-
Slow-Healing Wounds
High blood sugar damages blood vessels and nerves, hindering the body’s ability to heal cuts and infections.
-
Numbness or Tingling
Poor circulation and nerve damage can cause numbness or tingling sensations, particularly in the hands and feet.